Light/Heavy Industry

| HEX Type: | GPHE, BPHE, Welded, Semi-welded HEX |
| Plate Material: | Stainless Steel 304, 316L , 904L, SMO254, Titanium, HC276 |
| Plate Thickness: | 0.4mm-1.2mm |
| Gasket Material: | NBR, EPDM, HNBR, Viton/FKM |
| Frame Material: | Carbon steel , Stainless steel |
| Design Temperature: | -20~200℃ |
| Design Pressure: | 0-25bar |
Product Description
Plate heat exchangers play an important role in light and heavy industries such as pharmaceuticals and textiles. Why do most industrial heat exchangers choose plate heat exchanger instead of tube heat exchanger?
The plate heat exchanger has the function of heat exchange (heating, preheating, cooling, condensing). As long as it is the heat exchange between liquid-vapor and liquid-liquid, the plate heat exchanger can be used.
In this era of “energy saving and consumption reduction”, which is also a major strategic issue in the new era, the role of plate heat exchangers in this area can not be ignored by any relevant enterprise, because it is related to their cost and profit, so every enterprise that wants to save energy and reduce consumption must be taken seriously.
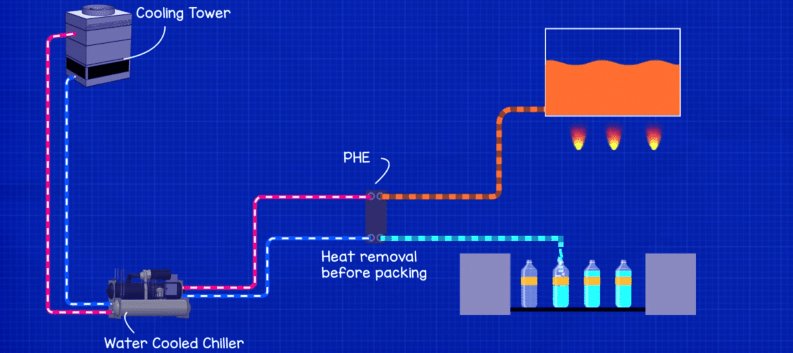
Many industrial plants will use plate heat exchangers for things such as pasteurization and waste heat recovery. For example a manufacturing plant may use water to cool down a hot, newly manufactured beverage product. The hot finished liquid product needs to be cooled down before bottling so it passes through a plate heat exchanger which is connected to the cooling circuit of a chiller. This extracts the unwanted heat without the two fluids mixing.
Pros and cons of using gasket type:
Pros: Can be dismantled for cleaning. Heating/cooling capacity can be changed. Parts can be quickly replaced if damaged.
Cons: leaks are rare but more likely due to the gaskets, higher pressure drop than shell and tube.